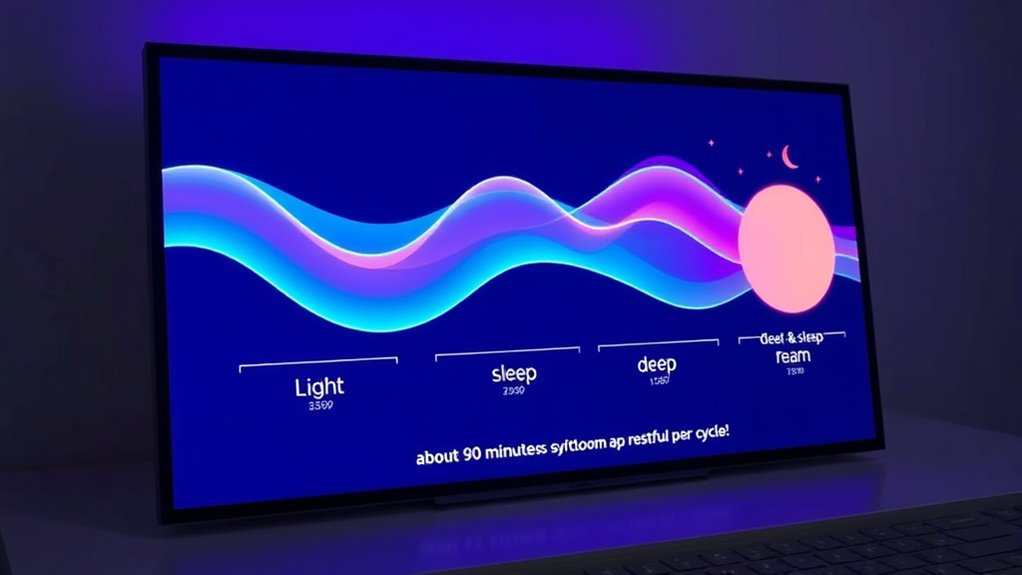
Your sleep typically consists of 4 to 6 cycles per night, each lasting 90 to 120 minutes. During each cycle, you go through stages: light sleep (5-10 minutes), deep sleep (20-40 minutes), and REM sleep (10-30 minutes). As the night progresses, REM periods get longer, and deep sleep becomes less frequent. Understanding these patterns can help improve your rest—keep exploring to discover how to optimize your sleep cycle.
Key Takeaways
- Most adults experience 4 to 6 sleep cycles per night, each lasting approximately 90-120 minutes.
- Each sleep cycle includes stages: light sleep, deep sleep, and REM, with REM becoming longer in later cycles.
- Deep sleep (NREM Stage 3) lasts about 20-40 minutes per cycle and is crucial for physical recovery.
- REM sleep lasts about 10-30 minutes initially, increasing in duration during later cycles.
- Sleep cycles evolve throughout the night, with early cycles dominated by deep sleep and later ones featuring longer REM periods.
The Stages of Sleep and Their Functions

Sleep occurs in distinct stages, each serving unique functions essential for your health. During the dreaming stage, your brain becomes highly active, and vivid dreams unfold as part of your sleep architecture. This stage helps process emotions, consolidate memories, and refresh your mind. The other stages include light sleep, where your body begins to relax, and deep sleep, which is indispensable for physical recovery and immune function. Understanding these stages reveals how your sleep cycles through different patterns throughout the night. Each stage plays a critical role, working together to restore your body and mind. Recognizing how the dreaming stage fits into this cycle highlights its significance in emotional regulation and memory retention, making your sleep both restorative and meaningful. Sleep architecture is a complex interplay of these stages that optimizes restorative processes during rest. Additionally, research indicates that completing multiple sleep cycles ensures that your body receives the necessary benefits of each stage for overall health.
Typical Number of Sleep Cycles per Night

On an average night, your body moves through multiple sleep cycles, each lasting about 90 to 120 minutes. Most adults experience four to six cycles per night, with REM sleep becoming longer and more frequent in later cycles. Adequate cycles are crucial for restorative rest, allowing your body to complete essential processes like memory consolidation and muscle repair. If you experience sleep deprivation, you might miss out on these cycles or spend less time in REM sleep, which impacts your mood and cognitive function. Additionally, the sleep architecture can be disrupted by poor sleep habits, affecting the overall quality of rest. Consistently getting enough sleep ensures you complete the typical number of cycles, helping you wake up refreshed. Skipping or shortening cycles can lead to feeling unrefreshed, emphasizing the importance of a full night’s sleep for overall health. Understanding sleep stages and their durations helps highlight the significance of uninterrupted sleep for optimal recovery. When your sleep cycles are disrupted or incomplete, it can interfere with restorative processes, leading to daytime fatigue and decreased mental clarity. Recognizing the influence of natural sleep patterns can further aid in achieving a healthier sleep cycle.
Duration of Each Sleep Stage
Understanding how long each sleep stage lasts can help you recognize the significance of a balanced sleep cycle. Typically, each cycle includes stages that vary in duration:
- Light sleep (NREM Stage 1) lasts about 5-10 minutes, easing you into sleep.
- Deep sleep (NREM Stage 3) spans 20-40 minutes, vital for physical restoration.
- REM sleep, where dream recall peaks, lasts around 10-30 minutes per cycle but can extend later in the night.
- Sleep cycle variability means these durations shift night to night, affecting how you experience dreams. Shorter or longer REM stages influence dream vividness and recall. Knowing this helps you understand why some mornings you remember dreams better than others, emphasizing the importance of consistent sleep for best cycle timing. Additionally, sleep architecture can be influenced by age, lifestyle, and health, further impacting your overall sleep quality.
How Sleep Cycles Change Throughout the Night

Have you ever noticed that your dreams tend to become more vivid or strange as the night progresses? That’s because sleep cycle variations occur throughout the night. Early in the night, your sleep is dominated by deep NREM stages, making dream recall less likely. As the night advances, REM sleep periods lengthen, increasing the chance of vivid dreams and better dream recall. These shifts mean your sleep cycles aren’t static; they change in duration and intensity, affecting how you experience sleep. Understanding how sleep cycles evolve helps explain why your sleep feels different across the night and highlights the importance of uninterrupted sleep for restorative rest. Sleep stage progression can even be influenced by Smart home technology that adjusts lighting and temperature to support healthy sleep cycles.
Factors Influencing Sleep Cycle Patterns

Your age can profoundly shape your sleep architecture, affecting how your sleep cycles progress. Lifestyle choices, like stress levels and activity habits, also play an essential role in your sleep quality. Recognizing these factors helps you understand what influences your sleep patterns and how you might improve them.
Age and Sleep Architecture
As you age, your sleep architecture undergoes significant changes that influence your sleep cycle patterns. These aging effects reflect ongoing sleep maturation, leading to notable shifts. Imagine this:
- Your deep sleep stages shrink, making way for lighter, more fragmented sleep.
- REM sleep decreases in duration, affecting memory and mood.
- Wakefulness during the night increases, causing frequent awakenings.
- Sleep cycles become shorter, disrupting the natural rhythm you once had. Additionally, alterations in sleep stages and patterns are associated with changes in brain activity and overall health.
- Changes in sleep architecture are often associated with alterations in sleep stages and patterns. These shifts are a biological response that is part of the aging process, not merely a consequence of lifestyle or health conditions.
- Recognizing these age-related changes can help you adapt your sleep habits to improve rest quality. These changes are natural parts of aging, shaping how your body cycles through sleep stages. Understanding sleep maturation helps you recognize that these shifts aren’t just habits but a biological response. While they may impact rest quality, awareness can guide better sleep strategies at any age.
Lifestyle and Sleep Quality
Lifestyle choices play a essential role in shaping your sleep cycle patterns, directly impacting sleep quality and consistency. Good sleep hygiene—like maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding screens before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment—can enhance your sleep quality and help you experience more restorative cycles. When your sleep is consistent, you’re more likely to have vivid dream recall, which is linked to better REM sleep. Conversely, poor habits such as irregular bedtimes, caffeine, or alcohol can disrupt your sleep architecture, causing fragmented cycles and reducing overall restfulness. By consciously improving your sleep hygiene, you support healthier sleep cycles, leading to more restful nights and clearer dreams. Small lifestyle adjustments make a significant difference in how well you sleep.
Tips for Optimizing Your Sleep Cycles

To optimize your sleep cycles, establishing a consistent sleep schedule is essential. This helps your body align its internal clock, making each phase smoother. Additionally, focus on your sleep environment by ensuring your room is dark, quiet, and cool. Incorporate calming bedtime routines, like dimming lights and avoiding screens, to signal your body it’s time to wind down. Here are four tips to enhance your sleep quality:
- Set a regular bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends.
- Keep your sleep environment cool and free of noise.
- Establish a relaxing pre-sleep routine, such as reading or gentle stretching.
- Limit screen time at least an hour before bed to reduce blue light exposure.
These steps help your body transition seamlessly through sleep stages, improving overall rest and supporting your inner wisdom and personal growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Sleep Disorders Affect Sleep Cycle Patterns?
Sleep disorders disrupt your natural sleep cycle patterns, causing issues like dream interruptions and irregular sleep stages. With insomnia patterns, you struggle to fall or stay asleep, which shortens your REM and deep sleep phases. This prevents your body from completing necessary restorative cycles, leading to fatigue and impaired cognitive function. You might also experience more frequent awakenings, making it harder to achieve restorative sleep and disrupting your overall sleep quality.
Can Sleep Cycle Durations Vary Between Individuals?
Yes, sleep cycle durations can vary between individuals. Your personal sleep patterns are influenced by factors like age, lifestyle, and genetic factors, which can cause differences in how long each sleep stage lasts. Some people naturally have shorter or longer cycles, impacting the overall quality of their sleep. Recognizing these variations helps you understand your sleep needs better and can guide you toward healthier sleep habits.
What Role Do Age and Health Play in Sleep Stages?
Imagine your sleep as a gentle river flowing through different stages, shaped by your age and health. Aging effects can make this flow slower, shortening deep sleep and increasing lighter stages, while health issues like stress or illness disrupt the rhythm. You may find yourself waking more often or feeling less refreshed. Prioritizing good health helps maintain a smoother, more restorative sleep cycle, keeping your river flowing peacefully.
How Do Medications Influence Sleep Cycle Progression?
Medications can substantially influence your sleep cycle by causing medication side effects like drowsiness or insomnia, which may disrupt your natural sleep pattern. Some drugs suppress REM sleep or extend certain stages, leading to sleep cycle disruption. You should be aware that these effects vary depending on the medication type and dosage, so consulting your healthcare provider can help manage and minimize any negative impacts on your sleep quality.
Are There Differences in Sleep Cycles Between Genders?
Like a dance with different rhythms, gender differences influence your sleep cycles. Hormonal impacts, such as fluctuating estrogen and testosterone, shape how your body moves through sleep stages. You might experience variations in REM duration or deep sleep phases, depending on your gender. Embracing these natural differences helps you better understand your sleep patterns, guiding you toward more restful nights tailored to your unique biological tune.
Conclusion
Understanding your sleep cycles helps you make the most of your rest. By recognizing how each stage works and how your patterns change, you can tweak your habits for better sleep quality. Remember, Rome wasn’t built in a day—consistency is key. Prioritize good sleep practices, and you’ll find that catching those essential cycles becomes second nature. Sleep smarter, not harder, and wake up feeling refreshed and ready to take on the day.